Stomatitis
06.08.2024Stomatitis
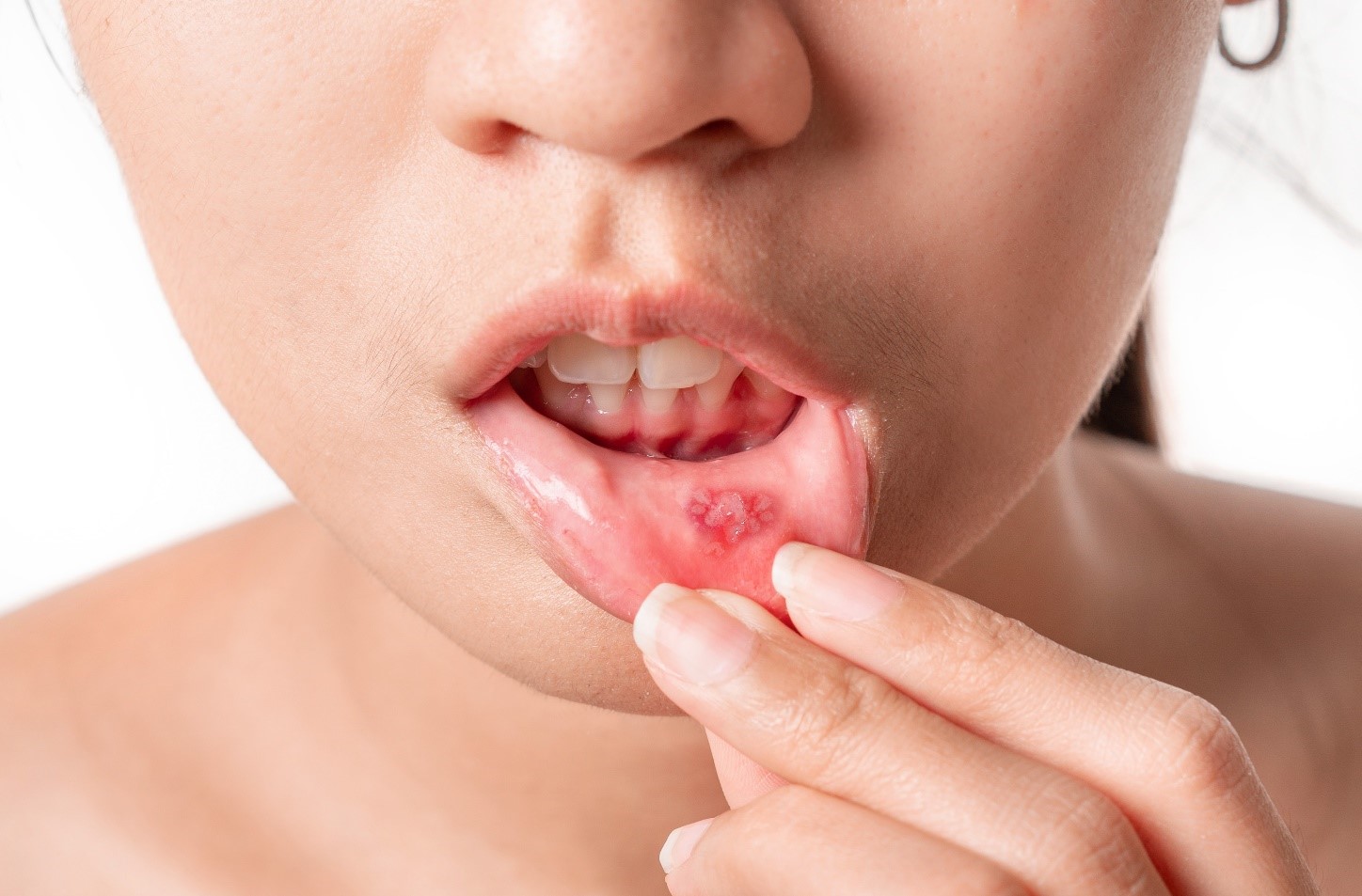
Stomatitis is inflammation of the mucous membrane in the mouth that can develop for various reasons. The main signs include pain, burning, redness, and ulcers in the mouth.
Main causes of stomatitis:
- Infections: viral, bacterial, or fungal infections.
- Trauma: injuries from teeth, consuming hot or hard food.
- Allergies: to food, medications, or other substances.
- Vitamin Deficiency: lack of vitamins and minerals.
- Autoimmune Diseases: immune system attacks the body's own tissues.
- Stress and Fatigue.
Treatment:
-
Infection Control: if the cause of stomatitis is an infection, antibiotics, antiviral, or antifungal medications may be needed.
-
Pain Relief: local anesthetics (sprays or ointments) can be used to relieve pain.
-
Hygienic Measures: regular oral hygiene, rinsing with solutions (e.g., salt or baking soda).
-
Preventing Damage: avoid hard or hot foods, use protective devices (e.g., mouthwash).
-
Vitamin Intake: consumption of vitamins and minerals such as vitamins A, B, C, and iron.
-
Consultation with a Doctor: if stomatitis frequently recurs or is severe, consulting a doctor is necessary to determine the cause and appropriate treatment.
If you have questions or need additional information, let me know.
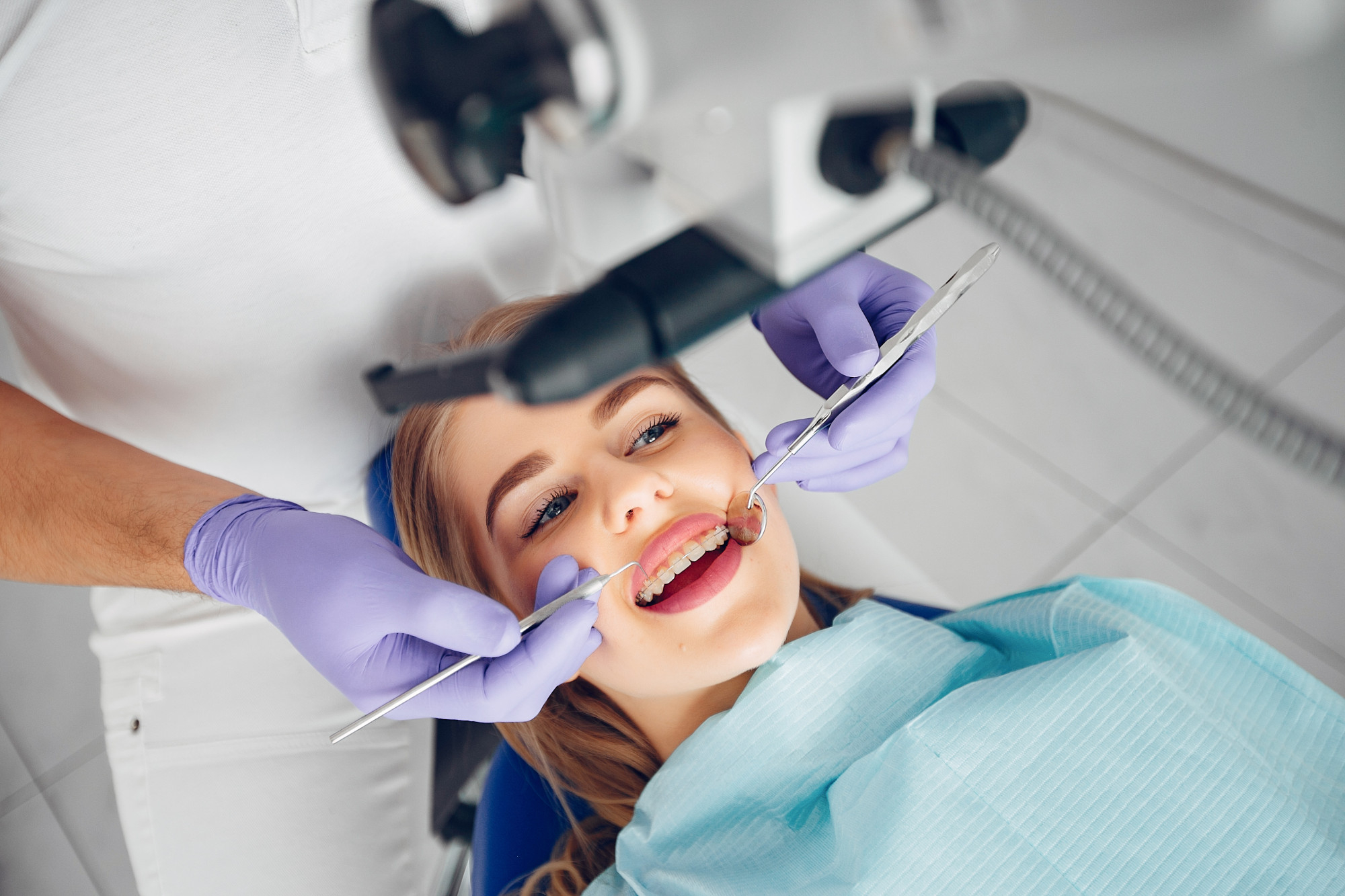
Role of the Doctor in Diagnosing and Treating Stomatitis
Diagnosis:
-
History Taking: the doctor will ask the patient about their medical history, symptoms, and signs to better understand the cause and progression of the disease.
-
Physical Examination: the doctor will carefully examine the mucous membrane of the mouth, ulcers, and lesions.
-
Laboratory Tests: if necessary, the doctor may order laboratory tests, such as blood tests, microbiological studies, and others.
Treatment:
-
Pharmacological Treatment: the doctor may prescribe antibiotics, antiviral, antifungal medications, painkillers, and anti-inflammatory drugs.
-
Topical Treatment: local anesthetics, antiseptic solutions, and ointments that act on the affected areas.
-
Recommendations: the doctor will investigate the causes of stomatitis and provide recommendations to prevent flare-ups and recurrence.
-
Monitoring Complications: the doctor will monitor and address complications of stomatitis, such as severe infection or tissue damage.
Prevention and Education:
-
Preventive Advice: the doctor will provide recommendations on oral hygiene, diet, and lifestyle to prevent stomatitis recurrence.
-
Follow-Up Visits: if necessary, the doctor will schedule regular check-ups to monitor the patient's condition and treatment progress.
-
Proper Nutrition and Vitamins: the doctor will recommend vitamins and minerals that support oral health.
Doctor intervention is especially important when stomatitis frequently recurs or is severe, as it may be a symptom of more serious diseases.